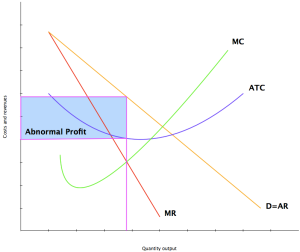
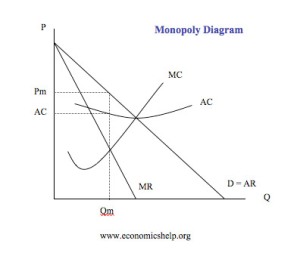
2a. Explain, using an appropriate diagram, how the monopolist determines the profit-maximizing level of output and price.
Monopolists determines the profit-maximizing level of output and price by producing where marginal costs = marginal revenue. Although this is similar for perfect competitions, however in a monopolistic market the demand curve is different therefor MC=MR is achieved in a different quantity.
2b. Discuss the view that competitive markets are always more efficient than monopolies.
In a competitive market, the firms are price takers. Therefor price always equals marginal cost therefor allocation efficiency is achieved. However in a monopolistic market firms are price givers. Firms set their price so that it is lower than the marginal cost, which means goods are under produced therefor not allowing allocation efficiency to be met.
6. With the aid of at least one diagram, explain one way a consumer might gain from the behaviour of a monopolist and one way a consumer might lose from the behaviour of a monopolist.
In an monopoly, a firm can decide to start engaging in price discrimination. For example, Jal conducts third-degree discrimination in which the price of a plane ticket differs according to your age. This profits customers as the plane ticket becomes affordable for a wider range of people.
Customers can also lose from an monopolist company. Since an monopolistic market has barely any competition, firms can decide to stop innovating and instead to just keep increasing their price. This would be detrimental for customers as they have no other substitute goods to buy from and instead would have to keep buying from the same firm.